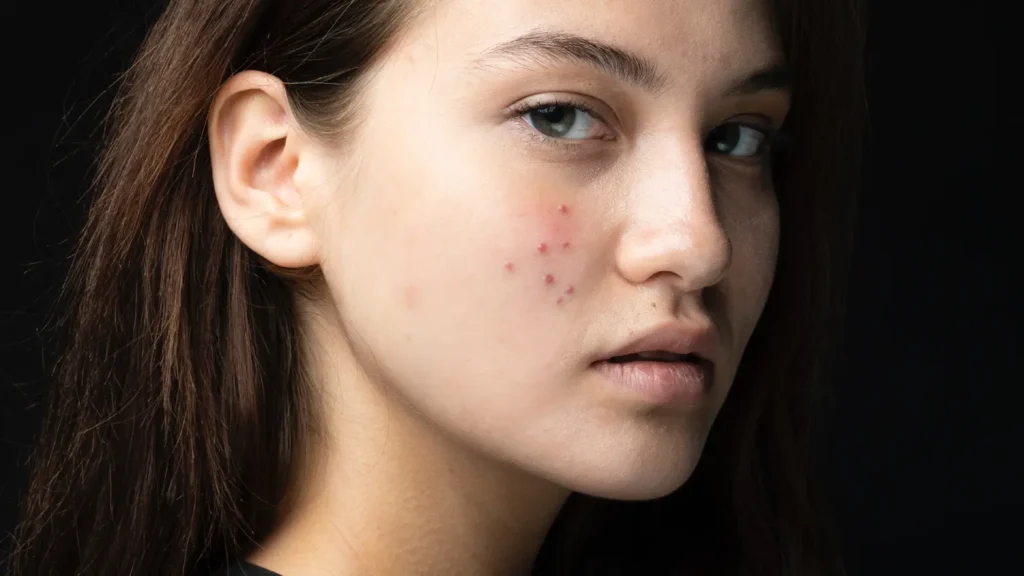
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Bacterial acne is particularly persistent, painful, and difficult to manage. Understanding what causes bacterial acne can help you find effective treatments to achieve clearer, healthier skin.
What Causes Bacterial Acne?
Bacterial acne primarily results from the proliferation of bacteria called Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) within the skin’s hair follicles. Several factors contribute to the development and exacerbation of bacterial acne:
- Excess Sebum Production: Overactive sebaceous glands produce excess oil, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
- Clogged Pores: Dead skin cells and oil can block hair follicles, trapping bacteria and leading to inflammation and infection.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, menstruation, or due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can increase sebum production.
- Diet and Lifestyle: High-glycemic diets, stress, and lack of proper skincare can worsen acne.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can increase your likelihood of developing the condition.
Treatments for Bacterial Acne
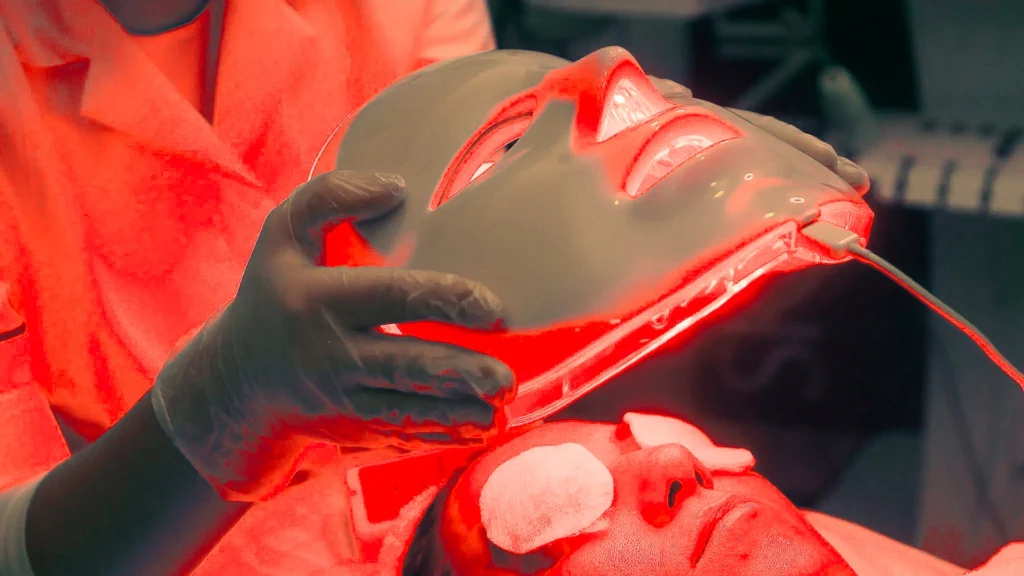
Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy (RLT) involves exposing the skin to low levels of red or near-infrared light. This treatment has gained popularity for its ability to reduce inflammation and promote healing. For bacterial acne, red light therapy can:
- Reduce Inflammation: Calming inflamed skin and reducing redness.
- Kill Bacteria: Penetrating the skin to kill P. acnes bacteria.
- Promote Healing: Encouraging the repair and regeneration of damaged skin.
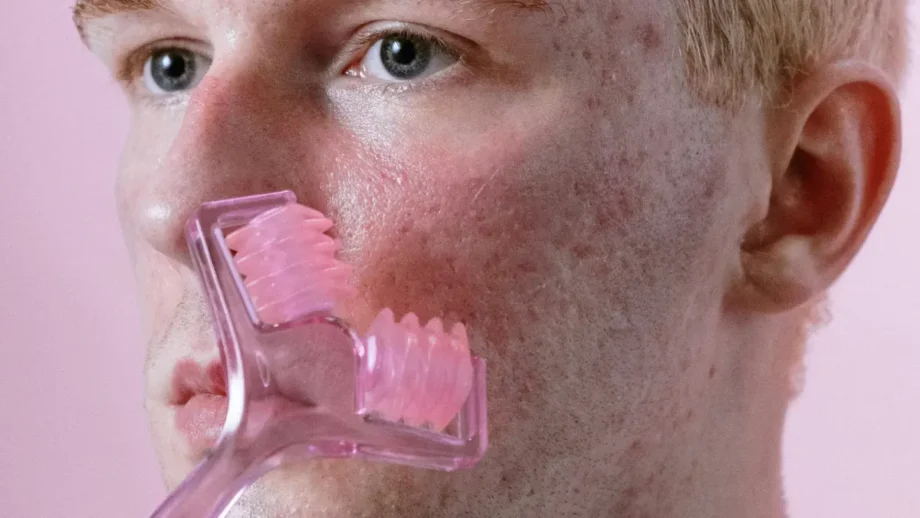
Microcurrent Therapy
Microcurrent therapy uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate cellular activity and enhance skin healing. It can help reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation, and promote collagen production. Microcurrent facials can benefit bacterial acne by improving immune response and accelerating the healing of acne lesions.
- Cellular Regeneration: Microcurrent therapy is believed to work by stimulating cellular activity, enhancing ATP production, and improving cellular repair and regeneration processes.
- Wound Healing: There is evidence suggesting that microcurrent therapy can accelerate wound healing, which may reduce bacterial acne by healing & reducing acne breakouts faster.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are a common and effective treatment for bacterial acne. They work by reducing the population of P. acnes bacteria and decreasing inflammation. Antibiotics can be administered both topically and orally:
- Topical Antibiotics: Creams or gels applied directly to the skin, such as clindamycin and erythromycin.
- Oral Antibiotics: Pills taken by mouth, including tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline.
Bacterial acne can be frustrating, but understanding its causes and exploring various treatment options can help you manage and reduce breakouts. Microcurrent therapy, red light therapy, and antibiotics are among the effective treatments that can be tailored to your specific needs. Consulting with a dermatologist will provide you with a personalized treatment plan to achieve clearer, healthier skin.
This article is brought to you by

Learn More ⭢